reading-note
html elements
- HTML elements are used to describe the structure of the page (e.g. headings, subheadings, paragraphs).
- They also provide semantic information (e.g. where emphasis should be placed, the definition of any acronyms used, when given text is a quotation).
There are lots of occasions when we
need to use lists. HTML provides us with
three different types:
- Ordered lists are lists where each item in the list is numbered. For example, the list might be a set of steps for a recipe that must be performed in order, or a legal contract where each point needs to be identified by a section number.
- Unordered lists are lists that begin with a bullet point (rather than characters that indicate order).
- Definition lists are made up of a set of terms along with the definitions for each of those terms.
The CSS Box Model
In CSS, the term “box model” is used when talking about design and layout.
The CSS box model is essentially a box that wraps around every HTML element. It consists of: margins, borders, padding, and the actual content. The image below illustrates the box model:
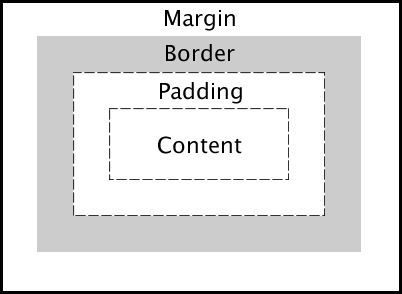 Explanation of the different parts:
Explanation of the different parts:
- Content :The content of the box, where text and images appear
- Padding : Clears an area around the content. The padding is transparent
- Border :A border that goes around the padding and content
- Margin : Clears an area outside the border. The margin is transparent The box model allows us to add a border around elements, and to define space between elements
JavaScript Loops
Loops are handy, if you want to run the same code over and over again, each time with a different value.
Often this is the case when working with arrays:
Instead of writing:
text += cars[0] + “
”;
text += cars[1] + “
”;
text += cars[2] + “
”;
text += cars[3] + “
”;
text += cars[4] + “
”;
text += cars[5] + “
”;
You can write:
var i;
for (i = 0; i < cars.length; i++) {
text += cars[i] + “
”;
}
Different Kinds of Loops
JavaScript supports different kinds of loops:
- for :loops through a block of code a number of times
- for/in : loops through the properties of an object
- for/of : loops through the values of an iterable object
- while : loops through a block of code while a specified condition is true
- do/while : also loops through a block of code while a specified condition is true